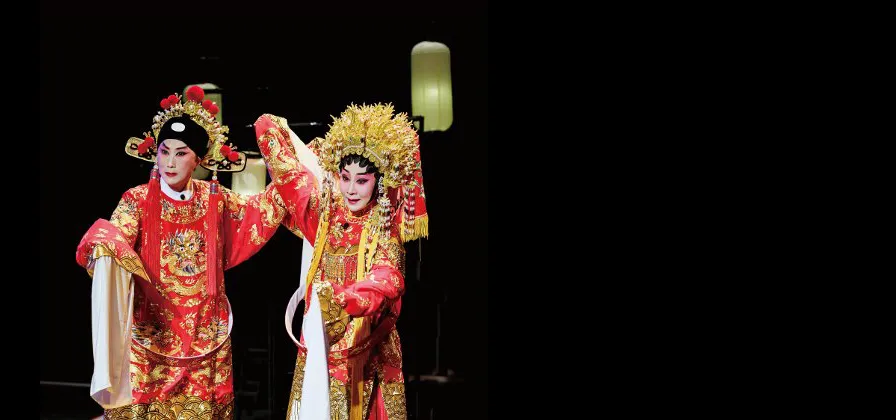
Black box theater and Chinese opera, what’s not to like?
The iridescent opera costumes are opulent against the backdrop of black box theater, yet at times, at the lower registers especially, you lose the words sung on the cavernous stage. Such are the lessons of Star Theatre’s third annual Xiqu Opera Black Box Festival in Beijing, held from October to the last week of December, 2016; in the formidable undertaking of making contemporary adaptations to millennia-old Chinese art forms, you win some and lose some.
The festival’s Chinese translation for “black box” is, literally, “small theater” ( 小剧场 ). It’s not exactly accurate, since black box theater primarily tends to be defined not by size as much as by an unadorned, streamlined look and flexible use of space, as the arrangement of the seats are not fixed and can be changed as needed. In this year’s festival, 17 out of the 19 official selections played in Star Theatre’s two biggest auditoriums, boasting more than plush 200 seats each, with an audience seated on one side as with the traditional proscenium stage.
In this case, explains Hu Hanchi, a student director whose work was featured in this year’s festival, black box or “small theater” ought to be interpreted in a relative sense. “It’s not the space getting smaller, people getting fewer, but it refers to a closeness of performers to the audience,” he says. “It’s about getting close enough to see what the creator wants to express.” At the Xiqu Opera Festival, this comes of playing directly on the auditorium floor, using minimal sets and technical distractions, and by creatively reimagining of the boundaries of the stage—including emotional boundaries.
Billed as an “experimental Kunqu opera” by the festival organizers, Hu’s work, Three Incarnations, is based on a story of the same name from Pu Songling’s Strange Tales from a Chinese Studio. In this tale, a man is able to recall three of his past lives—as a district magistrate, a dog, and an official overseeing the civil service examination—and comes into conflict with the same individual in each life. In terms of its themes and presentation, Hu’s piece holds perhaps the middle ground among the festival’s selected works. The official selection ran the gamut of ancient theatrical and operatic works garnished with a few lines of modern vernacular for comic effect to full postmodern productions, where traditional operatic themes are just some of the many cultural references made alongside hip hop, internet slang, and belly dance.
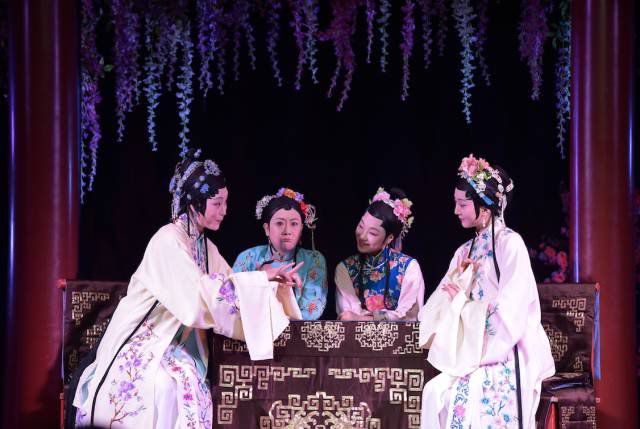

The opera Two Belles in Love reinterprets Qing dramatist Li Yu’s The Fragment Companion as a love story between the two female leads (Courtesy of Star Theatre)
For Hu, Three Incarnations was ideal meat for black box theater, being a work with an introspective theme and extremely limited cast. As a matter of fact, he is the only performer in his production, as well as the director and one of two co-writers.
He is also one of only two works at this year’s festival (along with a children’s opera) that played in a small auditorium with a “fan-shaped” stage, which has the audience seated on three sides and allows greater freedom with the performers’ use of direction and space.
By changing the original story’s three past lives to horse, dog, and snake, Hu allows himself to make more innovative use of body movements—honed by years of punishingly comprehensive studies at the National Academy of Chinese Theatre Arts—as well as reimagine the function of stock opera roles sheng, dan, and chou as being analogous of the three lives in the story, suggesting a coexistence of different moral qualities in one person when all played by the single actor.
The rest of the Xiqu Opera Festival’s programming is a mix of adaptations to traditional works in the major operatic genres of Peking, Kunqu, Yue (Shaoxing), Gan, and Yue (Canton) genres, as well as more imaginative oeuvres such as a Chinese operainfused take on Shakespeare’s As You Like It and an ache lhamo production, sometimes called “Tibetan musical theater.” There is also the closing performance, Four Westward Dreams, an original production (very) loosely inspired by the works of 16th century playwright Tang Xianzu (汤显祖)—all of his works.
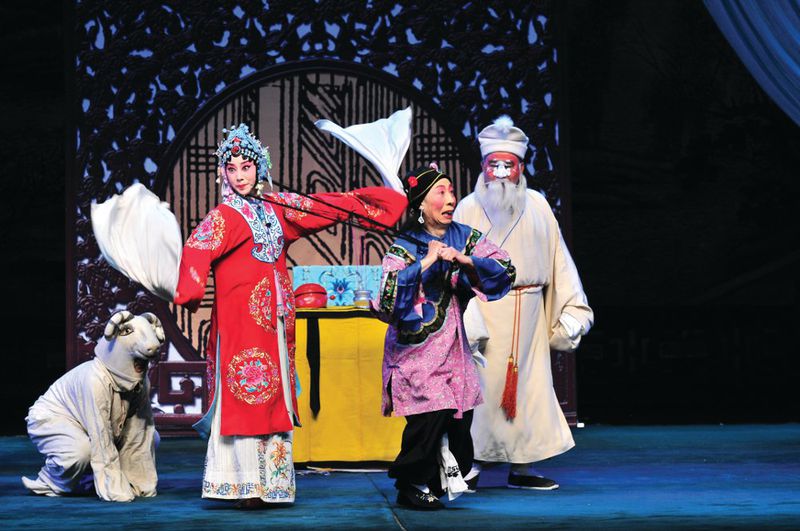

Some of the works performed at the festival are updated with humorous interludes and asides in modern spoken Chinese (Courtesy of Star Theatre)
In this last production, the festival somewhat falters. Opera influences are woven with fanatical care into the actors’ every movement and sustained note of their voice; the action primarily consists of pop culture-infused dialogue and dance numbers that are meant to take you out of the action and mirror the jarring, absurd changes of scenery and mood that everyone experiences while dreaming.
They succeed all too well, eating up any attention the audience might give to the actors’ technical finesse and the play’s occasionally breathtaking visual tableaux, which are the typical takeaways of a Chinese opera performance and shown off to special advantage by the minimalist black box setting. As two students in the audience complained afterwards, “it was just a regular play”—and not one that had the stealthiest references or that advanced any sort of biting critique with its pastiche and parody.
The road to modernizing Chinese opera, to be fair, was never going to be easy. Throughout modern Chinese history, each generation has tried to reinterpret opera according to what were deemed to be the fundamental political and moral values of their era. In the Republic of China period, the art developed codified techniques, training schools, and classic repertoire in reflection of a society-wide push toward more “scientific” ways of practicing culture; purists then protested, citing how the old (and famously brutal) training system produced elite performers unmatched in level of skill and dedication to the craft. The infamous “Eight Model Operas” sanctioned during the Cultural Revolution were later repudiated for monotony and overt political messages pushed at the expense of artistic merit.
Black box, on the other hand, is a somewhat recent phenomenon, appearing in China for the first time in 1995. It is primarily associated with youth directors and audiences and cultivates a decidedly niche identity. It’s still much easier to find listing for performances on social media than major magazines and city entertainment guides, while the venues tend to cluster around art districts and, increasingly, commercial areas catering to “artistic youths.” According to Hu, the black box concept is only beginning to take hold in the world of opera, but, like all contemporary movements, it’s nothing more than an invitation to express the ideas of contemporary society.
“As a post-90s generation creator I want to honor the ancient heritage of opera, but I also personally feel like opera can be ‘cool,’ so my production company and I like to express our work that way,” he says. “On the other hand, traditional opera format is too immensely rich and complex, so our challenge was to adapt it fit the unusual themes of the story in order to express our iconoclastic personality.”
“The word ‘experimental,’ is not something I came up with, but a label the festival gave my show—but similarly, I feel like that’s all relative, that any creation is an experiment and any opera in a ‘small theater’ is already experimental,” Hu says.
Thinking Inside the Box is a story from our issue, “Taobao Town.” To read the entire issue, become a subscriber and receive the full magazine.